Fundamental Idea:
These are another type of Data Structures. All operations have an average and worst case Time Complexity of .
BSTs must maintain specific properties in order to keep them efficient. If they break a property, they must be rebalanced - Rotated.
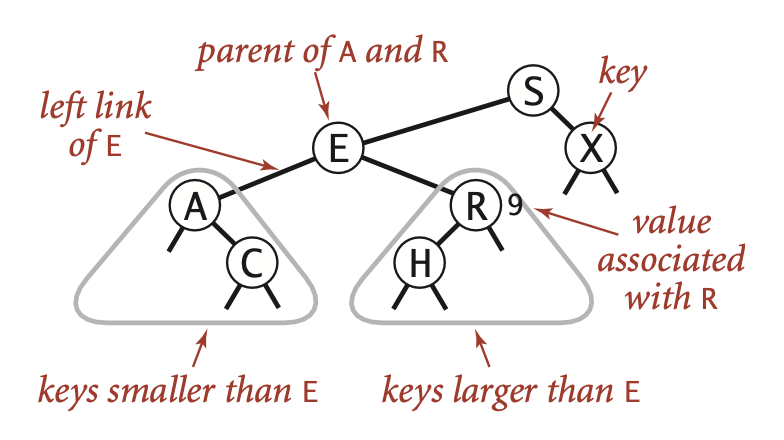
What Are Rotations?
This is altering the structure of the tree by rearranging subtrees, with the goal of decreasing the height of the tree. Crucially, rotations don’t affect the order of elements.
Right Rotations:
y x
/ \ / \
x C ==> A y
/ \ / \
A B B C- You take the node you want to perform a rotation on (E.G. y)
- You swing it down to the right and takes the place of what was there (B in this case).
- Whatever was there (B) now gets thrown onto the left of the node that got swung down (y)
Left Rotations:
Literally the same, just the opposite.
x y
/ \ / \
A y ==> x C
/ \ / \
B C A BLeft - Right Rotation:
z z y
/ \ / \ / \
x D y D / \
/ \ ==> / \ ==> x z
A y x C / \ / \
/ \ / \ A B C D
B C A BRight Left - Rotation:
x x y
/ \ / \ / \
A z A y / \
/ \ ==> / \ ==> x z
y D B z / \ / \
/ \ / \ A B C D
B C C DRed-Black Search Tree:
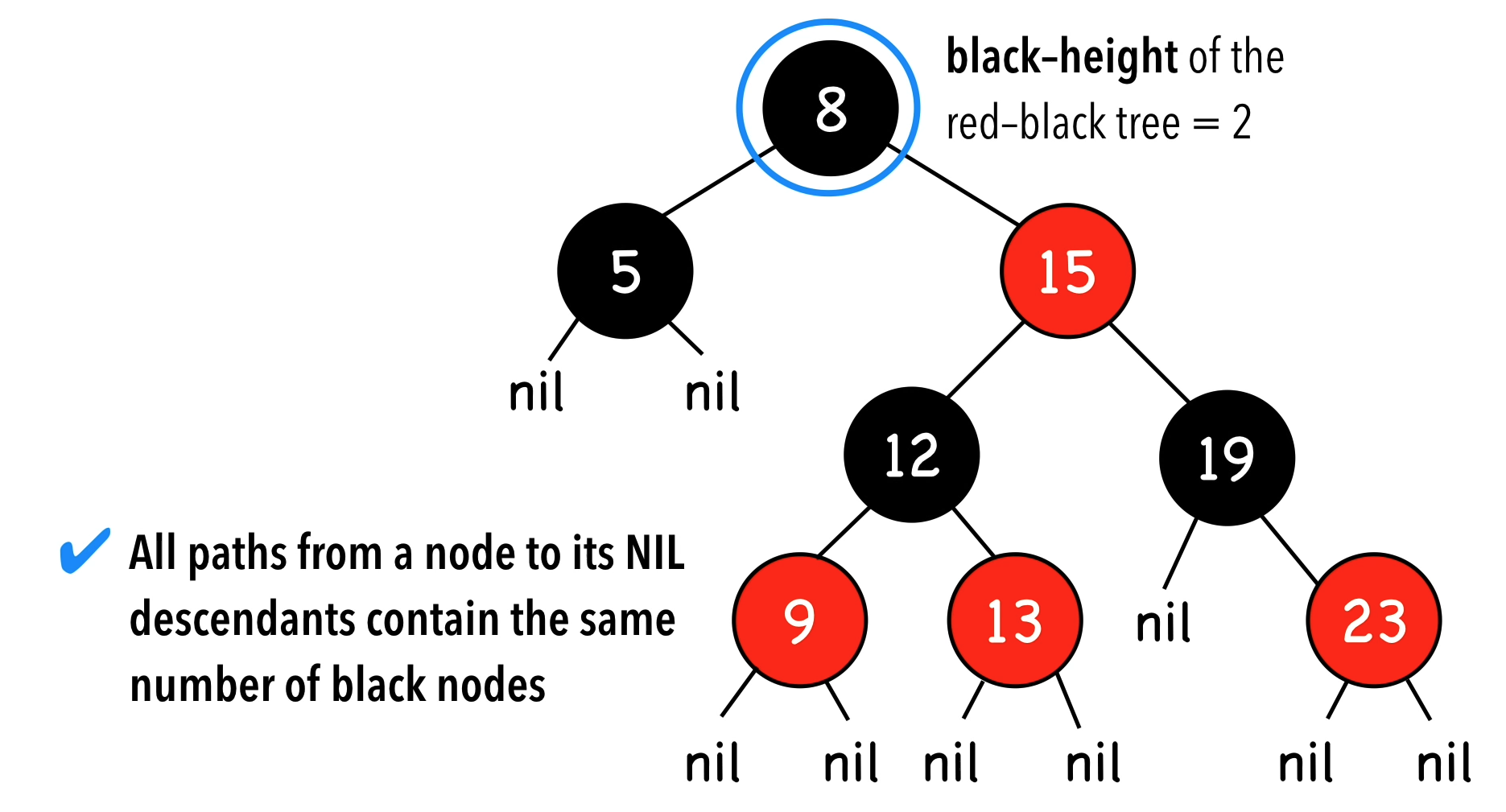
Criteria:
- A specific type of BST.
- Node is either red or black
- The root (top/base) and leaves (the very last nodes at bottom - NIL) are black.
- If a node is red, then its children are black
- All paths from a node to it’s NIL descendants contain the same amount of black nodes.
- This is also known as the “Black-height of the red-black tree”.
- You don’t count the starting node.
- The path to the farthest NIL is never more than twice the length to the shortest NIL.
Strategy for Insertion in RB Tree:
- Insert desired node and colour it red
- Recolour and rotate the rest of the nodes to adjust for any potential violations
