What
Stores shit.
Relational Databases
They’re databases stores info in tables with existing relationships between them. They use SQL for querying and managing the data. They ensure data integrity through relationships, constraints and normalisation.
Example
1. Users Table
| UserID | Username | DateCreated | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | JohnDoe | john@example.com | 2023-01-15 |
| 2 | JaneSmith | jane@example.com | 2023-02-20 |
| 3 | MikeJones | mike@example.com | 2023-03-10 |
2. Products Table
| ProductID | ProductName | Price | Category |
|---|---|---|---|
| 101 | Laptop | 800 | Electronics |
| 102 | Headphones | 100 | Electronics |
| 103 | Coffee Mug | 15 | Kitchen |
3. Orders Table
| OrderID | UserID | OrderDate | TotalAmount |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1001 | 1 | 2023-03-01 | 815 |
| 1002 | 2 | 2023-03-05 | 100 |
| 1003 | 1 | 2023-03-12 | 15 |
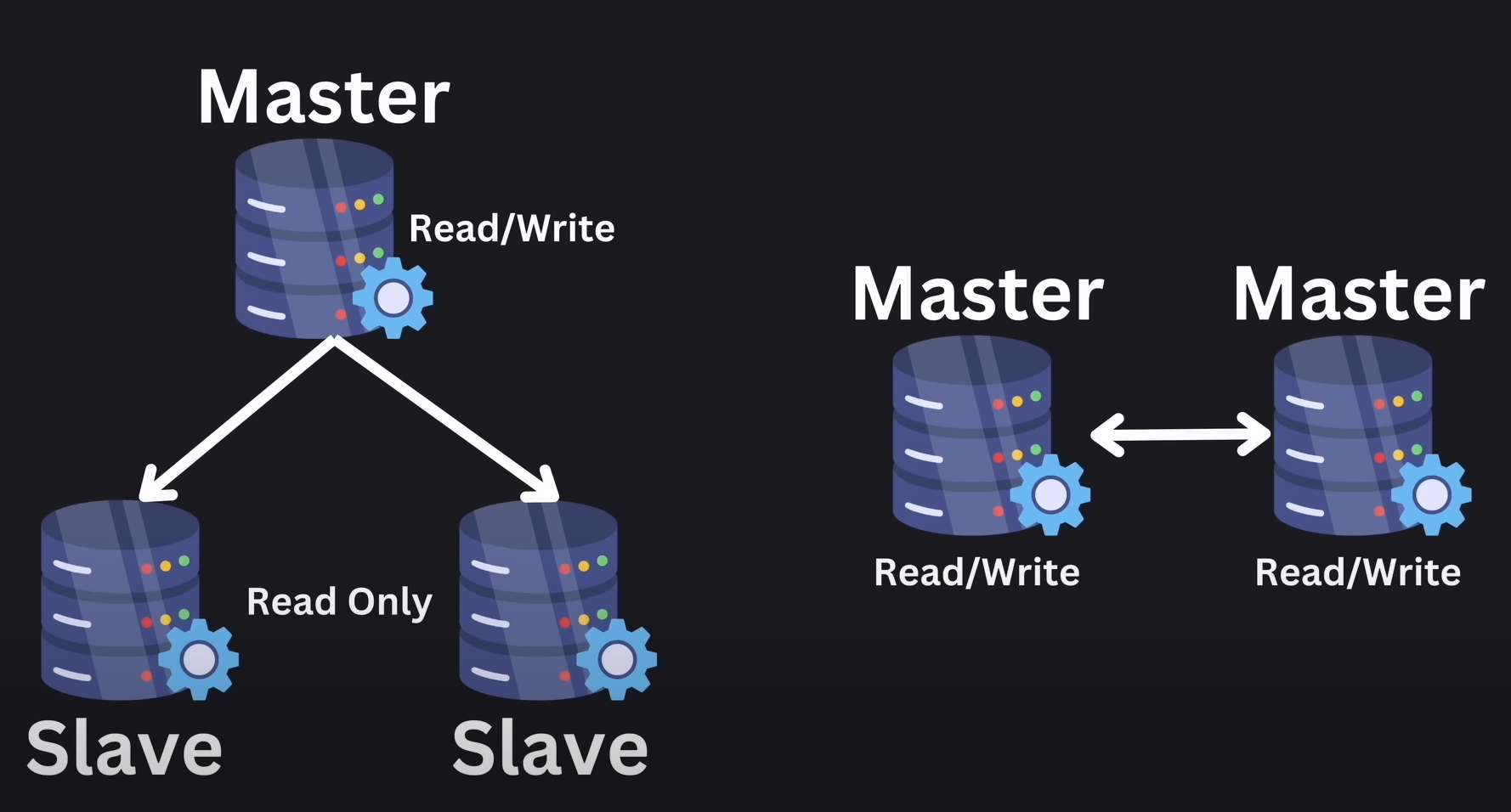
Scaling Databases
Horizontal Scaling:
Take a database and, instead of beefing up a single database, you add more databases to help it.
-
Sharding: You split up the data into multiple different databases, and ensure the indexing matches.
-
Replication: Basically, just have multiple different databases with identical information.
-
Quick Accessing of Databses
- Caching
- Indexing
- Query Optimisation