What are they?
- Simply: Physical implementations of Boolean Functions.
Examples:
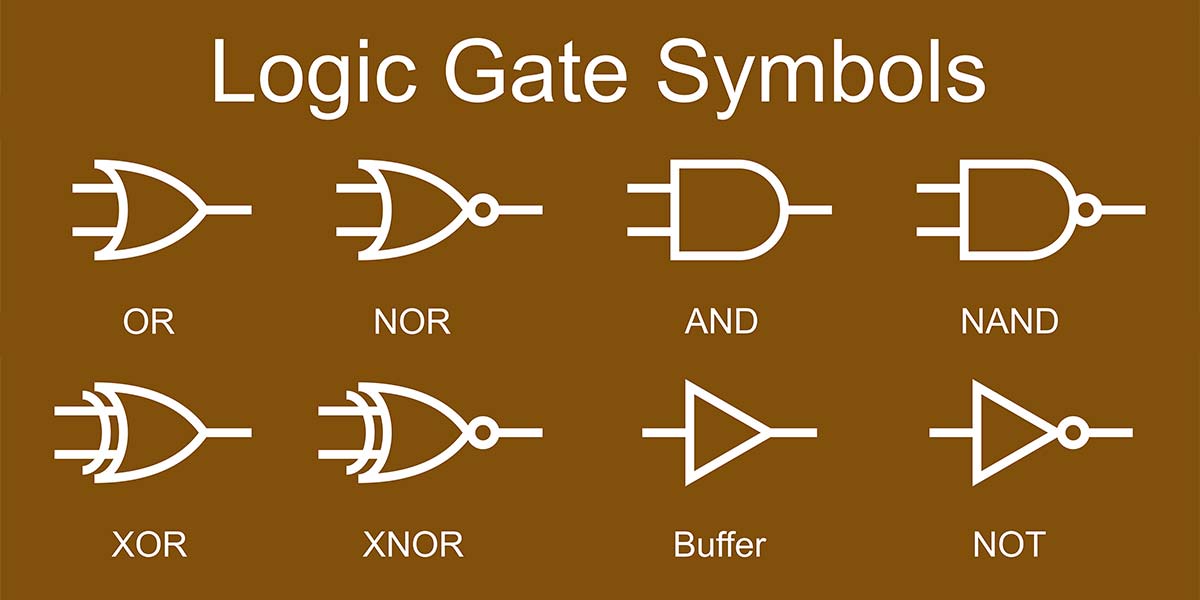
- AND Gate: Outputs true (1) only if all the inputs are true.
- OR Gate: Outputs true if at least one of the inputs is true.
- NOT Gate (also known as an inverter): Outputs the opposite of the input; if the input is true, it outputs false, and vice versa.
- NAND Gate: Outputs the opposite of the AND gate; it outputs true if at least one input is false.
- Fun fact: You can make any other gate by just using a collection of these.
- NOR Gate: Outputs true only if all inputs are false.
- XOR Gate (Exclusive OR): Outputs true if the inputs are different.
- XNOR Gate (Exclusive NOR): Outputs true if the inputs are the same.
- Multi-Input Gate: You can have both and and or gates. It would be true if all inputs are true or at least one is respectively.
Functionally Complete
It’s the idea that anything can be logically created from the most basic barebones.
EG: Any logical function can be made from:
{AND, NOT}{OR, NOT}{NAND}{NOR}