Why:
When writing Graphs into code, we need to represent them somehow.
Representing Graphs
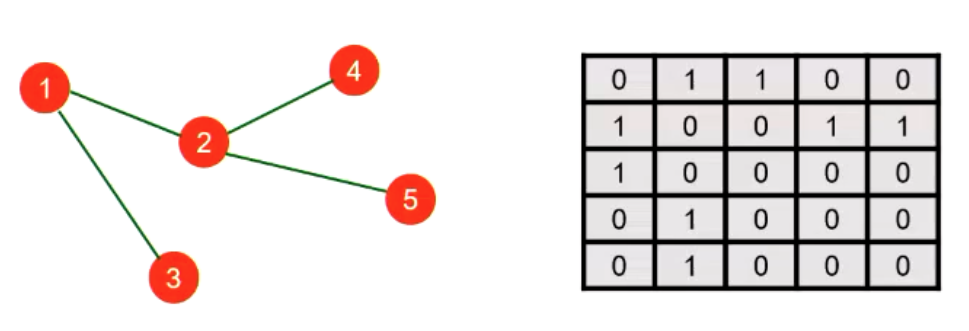
Adjacency Matrix
- The th node corresponds to the th row and the th column.
- Undirected graphs have . This is not necessarily the case for directed graphs.
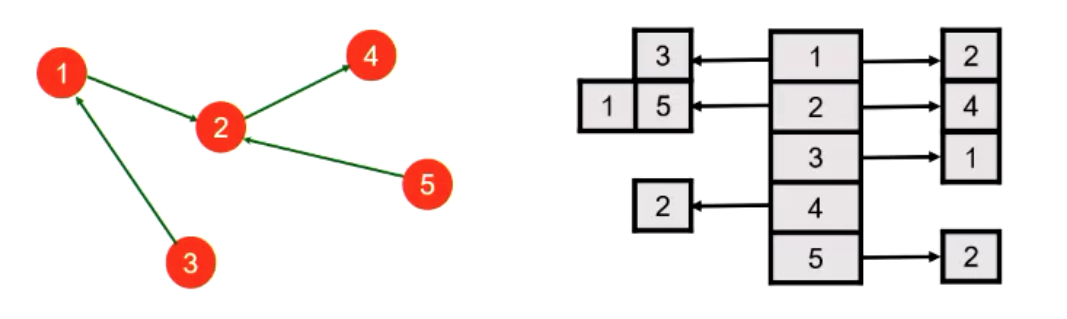
Adjacency List
- Nodes arranged as a list.
- Each list has a sublist of its neighbours.
Undirected Example: (Node 2 should also have neighbour 1)

Directed Example:
Complexities:
Adjacency Matrix
- Memory:
- Checking adjacency of u and v
- Time:
- Finding all adjacent nodes of u
- Time: O(n)
Adjacency List
- Memory: O(m+n)
- Checking adjacency of u and v
- Time:
- Finding all adjacent nodes of u
- Time:
- Better for: Sparse graphs, where the (nodes) >> (much larger) (number of edges.)