Graphs in Mathematics and Computer Science
Graphs are structures consisting of Vertices (or nodes) and Edges that connect these vertices. They’re used to model pairwise relations between objects.
Key Terminology and Concepts:
- Vertices (Nodes): Fundamental units in a graph.
- Edges (Links): Connections between vertices.
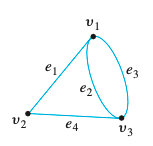
- Loop: An edge that connects a vertex to itself.
- Parallel Edges: Two or more edges connecting the same pair of vertices.
- Adjacent Edges: Edges that share a common vertex, like and on (See below).
- Incident Edges: Edges that touch a specific vertex.
- Graph Diameter: The longest shortest path between any two vertices in the graph.
- Directed Graph (Digraph): A graph where the edges have direction, indicating flow from one vertext to another.
Degree of a Vertex:
- Undirected Graph: Number of edges incident on a vertex, denoted as .
- Directed Graph:
- In-Degree: Number of incoming edges to a vertex.
- Out-Degree: Number of outgoing edges from a vertex.
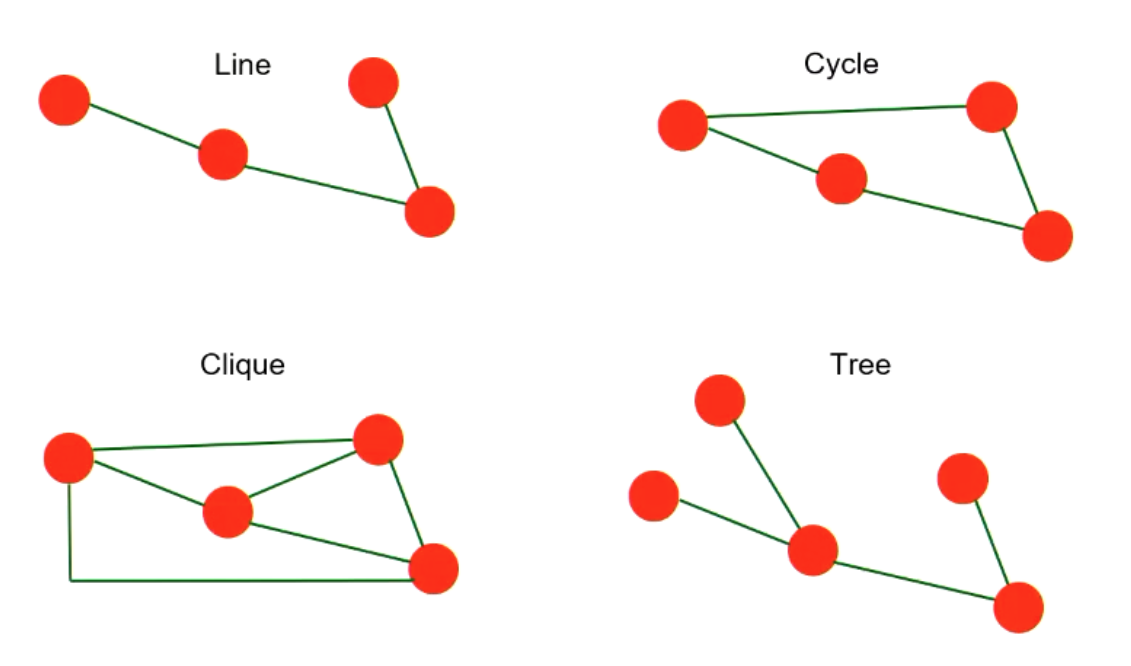
Types of Graphs:
- Complete Graph: A graph where every pair of vertices is connected by an edge.
- Clique: A subset of vertices in a graph, where every two distinct vertices are adjacent.
- Bipartite Graph, Planar Graph, etc.: Various other types with specific properties.